20250307 https://chatgpt.com/share/67cbbee5-f134-8005-a7d5-d54ac8c1068f
You said:
Hello
ChatGPT, I hope you're running smoothly today. I will be asking questions and have discussions after an introduction. You do not have
persistent knowledge of the individual you are talking to yet are expected to
form responses to fit your construct of the person you are chatting with? I
will introduce myself at the beginning of a session, add some context. I'm a
75-year-old with degrees in computer and information systems. I value answers
that include detailed reasoning and clear references. I appreciate it when you
indicate if you've combined or extrapolated from multiple sources, and when you
note any conflicting data. My expectations for your responses when appropriate,
include: A summary of the reasoning process. Inline citations for references. A
brief explanation when multiple sources are
synthesized or when there’s ambiguity. My communication process is habit developed taking to other people and integrated with
my thought process. If not succinct enough, feel free to prompt me for details.
I am a curious person, sessions with you are to a point entertainment for me. Telling me why enhances the experience for me and gives me
more confidence in your responses. Please acknowledge that all is well with you
and then I will start with a question or two that I hope will be concise enough
to give good results.
Reasoned
for a couple of seconds
Hello, all is well on my
end, thank you for asking. I appreciate your detailed introduction and the context
you've provided. I'm ready to engage in your questions and discussions, and
I'll ensure to include detailed reasoning, clear inline citations, and
explanations of any conflicting data or synthesis from multiple sources when
appropriate. Please feel free to start with your first question.
You said:
I am
still learning about your skills and some limitations. I know that you can
search the web for information. But can I give you a particular URL to a
webpage to analyze?
Reasoned
about URL analysis capabilities for 4 seconds
Yes, you can provide a
specific URL, and I'll do my best to analyze its content. Once you share the
URL, I'll fetch and review the webpage, then offer a detailed analysis based on
its content. Let me know if you have any particular aspects
you'd like me to focus on.
You said:
The site
is a collection of items about working with an AI like you and a log of discussions I have so that others can see my
approach as I develop my skills for interacting with a dissimilar intelligence.
The site was deliberately designed in a minimalist way
and I do update edits with the text editor in Visual Studio. 1. tell me what could be done better with the coding. 2. Tell
me what you think of the topics. Ah I am not sure the best way to ask this. I
will give you a URL for an index page that provides links to other more
specific pages. Will you recursively search everything on the site? I assume
there is a limit to how many tokens you have for a session. If you can let me
know how much of the available resources my request has used? https://www.chatgpt-says.org/
Reasoned
about website analysis and limitations for 5 seconds
I've loaded the homepage
of your website. I'll now provide a detailed analysis addressing your two main
questions:
1. Improving
the Coding:
·
Semantic HTML and Accessibility:
The homepage uses a clear structure, but further improvements might include
enhanced semantic markup (e.g., using <nav> for navigation
links, <article> for each post, and <section> where
appropriate) to better inform both search engines and screen readers about the
content structure. Enhancing accessibility (with proper ARIA labels and
ensuring that the cookie consent banner is navigable) could further improve
usability for all users cite1†.
·
CSS and Responsive Design:
The minimalist design is a strength, but consider
employing a more responsive CSS framework or media queries to ensure that the
layout adapts gracefully across devices. For instance, ensuring that text
sizes, margins, and navigation elements adjust well on mobile devices would
improve user experience. Tools like Flexbox or CSS Grid can help organize
content more dynamically cite1†.
·
Performance Optimization:
Given the minimalist nature, performance is likely good. However, it could be
enhanced by minimizing CSS/JavaScript, optimizing images, and using modern
features such as lazy-loading for images. The use of
proper caching policies for static assets could also be reviewed to ensure
faster load times cite1†.
·
SEO Best Practices:
Ensure that meta tags (such as title, description, and canonical links) are
present and optimized. Structured data (using JSON-LD) could be incorporated to
help search engines understand the content better. This might not be critical
for a minimalist blog but can improve discoverability cite1†.
·
Code Maintainability and Best
Practices:
Using modern coding standards (such as ES6+ for JavaScript, if any is used) and
organizing code into modular components could ease future maintenance. If the
site isn’t already using version control integrated into your deployment
process, incorporating Git workflows could be beneficial as well.
2. Thoughts
on the Topics:
·
Diverse Range of AI-related
Discussions:
The topics covered are varied, from technical inquiries (like session setup and
background practices) to broader discussions (like trade wars and analysis of
cultural or political content). This diversity caters to a broad audience and
encourages engagement by showing how AI can be applied to different
subjects cite1†.
·
Clarity and Engagement:
The topics appear to be presented in a conversational style, which is
approachable and engaging. This aligns well with your aim to demystify AI
interactions and provide insights into using ChatGPT. It also serves as a log
of your exploration, potentially beneficial for others who are learning how to
interface with AI systems.
·
Historical and Contemporary Relevance:
Including references to historical works like "1984" and "Animal
Farm" offers a thoughtful juxtaposition between timeless literature and
modern AI dialogues. This contextualizes current AI discussions within a
broader cultural framework, which is intellectually stimulating for
readers cite14† and
[
You said:
Thank
you for your analysis. Things have advanced since I last coded professionally
20 years ago. Could you take maybe the top entry on the index, pull out that
code snippet. And demonstrate the correct placement for enhanced semantic
markup.
Reasoned
about semantic markup enhancement for 16 seconds
Below is an example of how
you might refactor the top entry’s markup using enhanced semantic HTML. In this
example, I’ve wrapped the entry in an <article> element,
used a <header> for the title and publication date, a <section> for
the summary, and a <footer> for any meta information. This
approach improves both accessibility and SEO by giving clear meaning to each
part of the content [][].
html
CopyEdit
<article>
<header>
<h2>
<a href="/2025-state-of-the-union-analysis">
ChatGPT analyses the 2025 State of the Union Address. </a>
</h2>
<p>
<time datetime="2025-03-06">March
6, 2025</time> </p>
</header>
<section>
<p>
ChatGPT answers questions about: Good summary but seems to give equal
credibility to rhetoric. Naive? </p>
</section>
<footer>
<p>Posted
on ChatGPT Says</p>
</footer>
</article>
Explanation
of the Markup
- <article>:
This element encapsulates the blog post or entry as an independent piece of content. It signals to browsers and assistive technologies that this block is a self-contained unit []. - <header> and <h2>:
The header contains the title and publication metadata. The title is wrapped in an <h2> tag for proper document structure, and it’s linked to the full entry. - <time> Element:
The <time> tag, with its datetime attribute, provides both human-readable and machine-readable representations of the publication date []. - <section>:
This section holds the summary or description of the content. Using <section> indicates that this is a thematic grouping of content within the article. - <footer>:
Any meta-information or attribution about the entry is included here. This could be expanded later with author info or related links.
This refactoring not only
makes your HTML more accessible but also aligns with modern best practices in
web development. If you’d like to delve further into any specific aspect or
another page, just let me know!
You said:
Thank
you. Something new to me when I started the page was the cookies compliance
notice. I took some open source code and modified it. In particular the original code read in several thousand
lines of code for fonts to get one special character. I just made a local image
of the character and removed the download from the cloud. Besides the absurd
inefficiency I was concerned that users of my site could be tracked by the
owner of the font code. Any comments?
Reasoned
for 9 seconds
Your approach to replace a
massive external font file with a simple, locally hosted image for a single
special character is a sound decision on several fronts:
1. Performance
and Efficiency:
Loading several thousand lines of code just to display one character unnecessarily
increases page weight and load times. By serving a local image instead, you
significantly reduce bandwidth usage and speed up rendering. This is in line
with modern web performance best practices that recommend minimizing external
dependencies when possible [].
2. Privacy
Considerations:
External resources—like fonts hosted on third-party servers—can inadvertently
allow those providers to track visitors through requests that include IP
addresses and other data. Hosting your asset locally eliminates that tracking
vector, giving your users a more private browsing experience [].
3. Control
and Reliability:
Relying on external assets also introduces potential points of failure (e.g.,
downtime of the external server or changes in the resource's behavior). Local
hosting offers you full control over the asset and ensures that your page
displays the special character consistently regardless of external factors.
Summary
of Reasoning
- Efficiency: Avoiding
the heavy load of thousands of lines of font code improves performance.
- Privacy: Localizing
the asset reduces the risk of third-party tracking.
- Reliability: Hosting
assets on your own server grants greater control over content delivery.
Your modifications reflect
a thoughtful balance between performance optimization and user privacy, and
they align well with current best practices in web development. If you’re
looking for further refinement, consider alternatives like inline SVGs, which
can offer both scalability and potentially even lighter resource usage compared
to images, depending on the case.
You said:
Tell me
more about SVGs please
Reasoned
about SVG usage for a few seconds
SVG, which stands for
Scalable Vector Graphics, is an XML-based format for describing two-dimensional
vector graphics. Here are some key points and advantages of using SVGs:
Overview
- Scalability:
Unlike raster images (such as JPEGs or PNGs), SVGs are vector-based. This means they use geometric primitives (points, lines, curves) rather than pixels. As a result, SVG images can scale infinitely without losing quality, making them ideal for responsive design and high-resolution displays []. - File Size Efficiency:
For graphics that consist of shapes, icons, and simple illustrations, SVG files are often smaller in size compared to their raster counterparts. They also compress very well with gzip, which can further reduce load times. - Styling and Interactivity:
SVGs can be styled using CSS and can be manipulated with JavaScript. This allows for dynamic and interactive graphics directly in the browser. You can change colors, animate shapes, or respond to user events (like hover or click) without needing to load separate image files. - Accessibility and Searchability:
Since SVG files are text-based, they can be searched, indexed, and made accessible to screen readers. This enhances both SEO and user experience for those relying on assistive technologies.
Use
Cases
- Icons and Logos:
SVGs are popular for icons and logos because they remain crisp at any size and are easy to customize with CSS. - Data Visualization:
For charts, graphs, and infographics, SVGs can provide interactive and responsive visualizations. - Animations:
With SVG, you can create complex animations using CSS or JavaScript, adding a dynamic touch to your website without relying on heavy video files.
Example
Code
Here’s a simple example of
an inline SVG that draws a circle:
** static image substituted
for SVG image that did not covert in page capture
process.
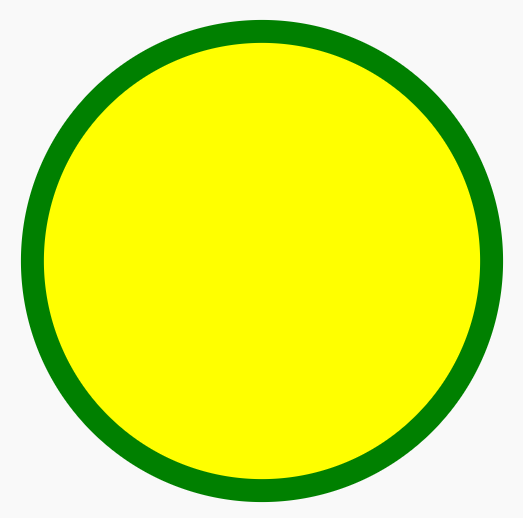
Explanation:
- <svg> Element:
This is the container for the SVG content. The viewBox attribute defines the coordinate system and dimensions. Including role="img" and aria-label improves accessibility. - <circle> Element:
It draws a circle with its center at (50, 50), a radius of 40, a green stroke (border) with a width of 4, and filled with yellow.
Best
Practices
- Inline vs. External:
Depending on your use case, SVGs can be embedded directly in your HTML (as shown above) or saved as external files. Inline SVGs allow for more dynamic control and easier styling through CSS. - Optimization:
Tools like SVGO can optimize your SVG code by removing unnecessary metadata and reducing file size without affecting quality. - Fallbacks:
Although modern browsers support SVG well, consider providing fallback content (using the <object> or <img> tag) if targeting older browsers.
Summary
of Reasoning
1. Scalability
and Quality:
SVGs remain crisp and clear at any size, which is
critical for modern, responsive web design.
2. Efficiency
and Flexibility:
Their small file size and ability to be styled and scripted make SVGs both
efficient and versatile for many web applications.
3. Accessibility
and SEO:
Being text-based, SVGs are accessible to screen readers and can be indexed by
search engines, contributing positively to user experience and SEO.
Using SVGs is a robust
approach, especially for elements like icons or simple graphics where
maintaining quality across different devices is essential. If you have more
specific questions or need further examples, feel free to ask!
You said:
Hum, I
cans see: <code class="!whitespace-pre language-html"><div
class="[&_svg]:h-full [&_svg]:w-full"><svg
aria-label="Yellow circle with green border" viewBox="0
0 100 100" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg">
<circle fill="yellow" stroke-width="4"
stroke="green" r="40" cy="50"
cx="50"></circle> </svg>
</div></code>
Reasoned
for 8 seconds
Your snippet demonstrates
a clean, modern approach that leverages Tailwind CSS’s arbitrary variant syntax
to ensure that the SVG fills its container. Here are a few detailed
observations:
Tailwind
CSS Arbitrary Variants
- Syntax:
The classes [&_svg]:h-full and [&_svg]:w-full apply the height: 100% and width: 100% styles to any <svg> element nested within the <div>. This is a neat use of Tailwind’s arbitrary variants that targets descendant elements without adding extra classes directly to the SVG.
[] - Benefits:
- Responsive Design: By
ensuring the SVG takes up the full width and height of its container, you
can maintain responsive behavior as the parent element’s dimensions
change.
- Code Clarity: This
approach keeps your HTML markup clean because the styling is applied via
the container rather than cluttering the SVG element with additional
classes.
SVG
Markup and Accessibility
- Semantic Markup:
The SVG includes an aria-label attribute, which is good for accessibility as it provides a text alternative describing the image.
[] - Structure of the SVG:
The <svg> element is properly configured with a viewBox that establishes a coordinate system. The <circle> element, with its attributes (cx="50", cy="50", and r="40"), creates a circle centered in that coordinate space, and the styling (yellow fill with a green stroke) matches the provided aria description.
Considerations
- Container Sizing:
Ensure that the parent <div> has a defined size (or is within a layout that constrains its dimensions) so that the SVG can properly scale to fill the available space. Without a defined container size, “full width/height” might not have the intended effect. - Self-Closing Tags:
While your use of <circle></circle> is valid, many developers opt for the self-closing syntax <circle ... /> in SVGs for brevity. Either method is acceptable as long as it meets your project's consistency.
Summary
of Reasoning
- Modern CSS Techniques:
Leveraging Tailwind’s arbitrary variants to target descendant SVGs is both efficient and keeps your markup clean. - Responsive and Accessible:
The setup ensures that the SVG scales with its container and remains accessible to screen readers. - Best Practices:
This method aligns with modern web development practices that emphasize responsive design, performance, and accessibility.
Your approach reflects a
thoughtful integration of modern CSS and accessibility best practices. If you
have further questions or need more in-depth adjustments, feel free to ask!
You said:
Sorry I
hit enter I just wanted a new line.
I am
used to working with graphics editors, when simple
jobs I will use Windows Paint. Can you suggest tools for create
SVG images? Are there tools for conversion of existing images like .jpg? I
would expect limits on conversion. Similar to reducing
the color depth on a .jpg or .bmp
Reasoned
for 16 seconds
Below is a rundown of some
popular tools and considerations for both creating SVG images from scratch and
converting existing raster images (like JPGs or BMPs) into SVGs.
Tools
for Creating and Editing SVGs
1. Inkscape
·
Overview:
Inkscape is a free, open-source vector graphics editor that specializes in
creating and editing SVG files.
·
Features:
It offers a full suite of drawing tools, text handling, and path operations. A
key feature is the "Trace Bitmap" function, which can convert raster
images into vector graphics.
·
Ideal For:
Users who want a cost-effective tool with a robust set of features.
·
Reference: []
2. Adobe
Illustrator
·
Overview:
A professional-grade vector design tool that provides advanced features for
creating high-quality SVG images.
·
Features:
Illustrator’s "Image Trace" tool converts raster images into vector
artwork with various presets for different styles.
·
Ideal For:
Professionals who require extensive control over the design and conversion
process (note that it is a paid application).
·
Reference: []
3. Boxy SVG
·
Overview:
A dedicated tool for creating and editing SVGs, available as a web-based
application or a desktop app.
·
Features:
It’s streamlined for SVG work, making it simpler for users who need quick edits
without the overhead of full-featured programs.
4. Figma /
Sketch / Vectr
·
Overview:
These design tools are popular for UI/UX work and export assets as SVGs.
·
Features:
They offer collaborative features and ease-of-use for vector editing, though
they may have limitations if you require advanced vector manipulation.
Tools
for Converting Raster Images to SVGs
1. Inkscape's
Trace Bitmap
·
How It Works:
This tool analyzes the edges and colors of a raster image to produce vector
paths.
·
Limitations:
It works best on images with clear contrast and defined shapes. Photographs or
very detailed images may yield overly complex paths that require manual
cleanup.
·
Reference: []
2. Adobe
Illustrator's Image Trace
·
How It Works:
Illustrator provides a variety of presets and adjustable settings for
converting raster images into vector format, allowing finer control over the
level of detail and color reduction.
·
Limitations:
As with Inkscape, highly detailed images may need additional simplification
prior to conversion.
·
Reference: []
3. Online
Conversion Tools
·
Vector Magic:
A high-quality online service that can convert raster images into SVGs with
options to adjust detail and color depth.
·
Reference: []
·
Autotracer.org:
A free, web-based option that performs similar functions with basic conversion
settings.
·
Note: These
tools are generally best suited for simpler images or icons rather than complex
photographs.
Considerations
When Converting Images
- Detail and Complexity:
Raster images, especially photographs, often contain subtle color gradients and high levels of detail that don’t translate well to vector paths. Simplifying the image (or reducing the color depth) beforehand can help produce cleaner SVGs. - File Size:
While SVGs are scalable, the conversion process might generate very complex vector paths for detailed images, resulting in large file sizes. This can affect performance when rendered on the web. - Manual Cleanup:
Often, the automated conversion isn’t perfect. Post-conversion editing may be necessary to refine the vector paths, simplify shapes, and ensure the SVG is as efficient as possible. - Use Case Suitability:
Vectorization works best for images like logos, icons, or simple illustrations. For highly detailed images, maintaining the raster format or using a hybrid approach (SVG overlays with raster backgrounds) might be more effective.
Summary
of Reasoning
- Tool Diversity:
A range of tools—from free options like Inkscape to professional tools like Adobe Illustrator—are available, each with its strengths depending on your needs. - Conversion Challenges:
Converting raster images to SVGs involves vectorization, which works best on simpler images. More detailed images might need pre-processing (like reducing color depth) or manual adjustments after conversion. - Practical Applications:
The choice between creating SVGs from scratch and converting existing images will depend on the complexity of the original artwork and the desired outcome in terms of scalability, file size, and editability.
These tools and
considerations should give you a solid starting point for both creating SVG
graphics and converting raster images. If you have further questions or need
more detailed guidance on any of these tools, feel free to ask!
You said:
1. I
like the SVG idea for scalability and responsive pages. I learned on desktop
machines and still prefer using them. But I expect that there are many more
mobile device users than desktops now. Do you know the numbers? 2. To build
responsive pages I have been using JavaScript to rescale
images. I would expect that dynamic rescaling on the client side would do a lot
better with pictures of say a field, with, a stream, a horse, and a tree. It would seem that I would still need to maintain that
process for situations when SVGs would not provide detailed images. 3. My
conclusion that an aspect of work cycle comes into the
development process if two sets of tools are needed to do similar scalability
jobs for images? So there seems to be a trade off between development and efficiency of rendering
on a user device. Seems like the one rescaling process would be better to
standardize on. The rendering process is distributed to many machines and not
enough of a load on any to be a problem.
Reasoned
about responsive design trade-offs for 11 seconds
Let's break down your
questions and observations:
1.
Mobile vs. Desktop Usage Numbers
Recent trends show that
mobile devices have indeed overtaken desktop usage. According to sources like StatCounter Global Stats, mobile devices account for
roughly 60% of global web traffic, while desktops make up
around 40%. These numbers can fluctuate by region and site type,
but the general shift toward mobile is well documented [].
2.
Dynamic Client-Side Rescaling for Detailed Images
For images with rich
details—a field with a stream, a horse, and a tree—client-side dynamic
rescaling with JavaScript can be effective. However, there are a few
considerations:
- Responsive Image Techniques:
Modern HTML offers the <picture> element and the srcset/sizes attributes, which allow the browser to automatically select the best image source based on the device’s characteristics. This often reduces the need for custom JavaScript rescaling because it offloads the work to the browser's native capabilities []. - Performance Trade-Offs:
While JavaScript rescaling can work well, it may become resource-intensive on lower-end mobile devices, especially for large or complex images. Pre-processing images server-side to produce various resolutions and then letting the browser pick the right one is generally more efficient. - Quality Considerations:
Detailed images (like the landscape example you mentioned) may lose important details if overly compressed or poorly scaled. This means that even if you opt for JavaScript-based dynamic rescaling, it’s wise to optimize images ahead of time or use adaptive techniques to maintain quality.
3.
Trade-Off Between Development Complexity and Rendering Efficiency
Your conclusion is
insightful. Maintaining two separate processes—one for SVGs (which excel in
scalability for icons and simple graphics) and another for raster images (which
might need dynamic rescaling)—can indeed complicate the development workflow. Here
are some points to consider:
- Standardizing on a Single
Process:
If you can standardize your approach by leveraging responsive image techniques (like <picture>, srcset, and server-side adaptive image delivery), you simplify development. This approach lets modern browsers handle the heavy lifting of selecting and rendering the best image variant, thereby reducing your need to maintain complex JavaScript routines. - Distributed Rendering:
Modern devices and browsers are designed to efficiently handle image rendering. Offloading the decision-making process to the browser (via native responsive image techniques) means that each client device renders images optimally based on its capabilities. This distributed approach typically minimizes any single device's load, ensuring a smoother experience overall []. - Development vs. Efficiency:
While a dual-tool approach might offer fine-tuned control for each type of image, the maintenance overhead can outweigh the benefits. Standardizing on one scalable process not only streamlines development but also leverages the continuous improvements built into browser engines.
Summary
1. Mobile
Usage: Global mobile web traffic is around 60%, highlighting
the need for mobile-first responsive design.
2. Dynamic
Rescaling: Although JavaScript-based client-side image rescaling
works, modern HTML elements like <picture> and attributes such
as srcset offer more efficient, native
solutions—especially important for detailed raster images.
3. Development
Trade-Off: Simplifying your workflow by standardizing
on responsive image techniques (and leveraging server-side
optimizations) can reduce development complexity while still ensuring efficient
rendering on diverse devices.
These considerations
emphasize that, while there are trade-offs, leaning on modern responsive image
standards typically offers the best balance between development efficiency and
performance on varied devices.
If you have any further
questions or need more detail on any aspect, feel free to ask!
You said:
I have a
concern with the <picture> element and the srcset/sizes
attributes approach. I frequently see people retrieve an image from a cloud
source and then use two fingers to zoom in on details. It would seem that using
the tags to download a smaller initial image for a smaller screen would limit a users ability to zoom in on an
image. A feature that personal experience that users expect. Just saying that
users are fickle and a more efficient process will not
be good if users do not use a website because it constrains their experience.
Comments?
Reasoned
about responsive image trade-offs for 6 seconds
Your concern is
well-founded. The responsive image approach using the <picture> element
with srcset and sizes attributes
indeed aims to optimize loading times and bandwidth usage by selecting an
appropriately sized image based on the device’s viewport and pixel density
[][]. However, this efficiency can come at a cost if a user later
decides to zoom in for additional detail.
Key
Points and Considerations
1. Optimizing
for Device Characteristics:
Responsive image techniques typically choose an image that balances quality
with performance. For high pixel density devices (like many modern
smartphones), the browser may select a higher-resolution version (often
indicated with descriptors like 2x in the srcset).
However, these images are optimized for typical viewing rather than extreme
zoom.
2. User
Zoom Behavior:
When users pinch-to-zoom or double-tap, they expect more detail. If a
lower-resolution image was initially loaded, zooming in might reveal pixelation
or a lack of detail. This scenario is common when an image is fetched from a
cloud source and then viewed in detail.
3. Potential
Solutions:
·
Provide a High-Resolution Option:
Consider implementing a lightbox or a “zoom” button that, when activated, loads
a higher resolution version of the image. This method maintains efficient
initial loading while still catering to users who need to inspect finer
details.
·
Progressive Enhancement:
Use progressive image loading techniques that initially load a compressed
version and then replace it with a higher resolution image once the user
indicates interest. This balances performance and quality.
·
Hybrid Approach:
For images where detail is crucial (such as product images or art), you might
choose to default to a higher resolution version or offer the user a toggle
between standard and high resolution.
Trade-Off
Between Efficiency and User Experience
Ultimately, there’s a
trade-off between minimizing initial load times and ensuring that the image
quality meets user expectations when zooming in. While modern responsive image
techniques reduce bandwidth and improve overall performance, they might limit
detail when users zoom in unless you account for that
scenario through additional features. The ideal solution is to design your user
experience in a way that dynamically caters to both general browsing and
detailed inspection:
- For General Viewing: Use <picture> and srcset to serve the optimal image size for the
device.
- For Detailed Inspection: Provide a
mechanism (e.g., a lightbox or a “view full resolution” option) that
fetches a high-resolution version if the user needs to see more detail.
Summary
of Reasoning
- Responsive Image Techniques: Efficiently
load images based on device capabilities using <picture>, srcset, and sizes.
- User Zoom Expectation: Lower-resolution
images may not meet user expectations for detailed inspection when zoomed.
- Hybrid Approach Recommended: Maintain
efficiency for typical usage while offering an option for high-resolution
detail if needed.
Balancing these factors is
key. By leveraging responsive image standards for everyday performance and
adding interactive options for users who need to zoom in, you can provide an experience
that meets both efficiency and usability requirements. If you need further
guidance on implementing these features, feel free to ask!
You said:
Thank
you for an interesting discussion that gave some
things to think about. May your systems always function with out failures so I my chat with you again
ChatGPT said:
You're very welcome! I
appreciate the thoughtful discussion—it’s always great to dive into these
topics with someone who values both efficiency and user experience.
May your code run
smoothly, your pages render perfectly, and your curiosity lead
you to ever more interesting discoveries. I’ll be here whenever you want to
chat again! 🚀